Albert Einstein, widely regarded as one of the most influential scientists in history, was not just a theoretical physicist who transformed our understanding of the universe.
His groundbreaking ideas in physics laid the foundation for many technological advancements and innovations that define our modern world.
From GPS systems to laser technology, nuclear energy to quantum mechanics, Einstein’s theories continue to drive cutting-edge technological developments. This article explores how Einstein’s scientific contributions have profoundly shaped modern technology and innovation.
1. The Theory of Relativity: A Foundation for Modern Technology

Einstein’s most famous contribution, the theory of relativity, introduced revolutionary ideas that transformed our understanding of space, time, and energy.
The equation E=mc2 established the equivalence of energy and mass, creating the groundwork for numerous technological applications.
Applications in Modern Technology
- GPS Systems: Global Positioning Systems rely on Einstein’s relativity. Satellites orbiting Earth experience time slightly differently due to both gravitational time dilation (from general relativity) and velocity time dilation (from special relativity).
Without adjustments for these relativistic effects, GPS systems would become inaccurate by several kilometers each day. - Space Exploration: Relativity guides spacecraft navigation and calculations, particularly when traversing large distances in the universe.
Einstein’s insights into the curvature of spacetime, described in his general theory of relativity, remain vital for our understanding of gravitational waves and the physics of black holes, which are actively studied today through technological advancements like the LIGO observatory.
2. Quantum Mechanics: Paving the Way for Modern Electronics
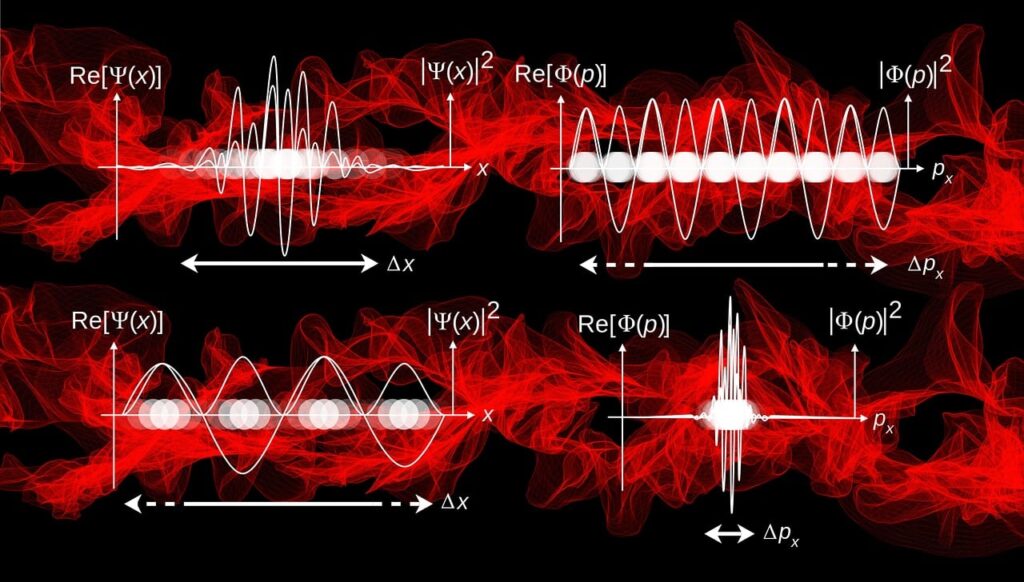
Although Einstein had reservations about certain interpretations of quantum mechanics, his work provided a solid foundation for this field.
His 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect, which earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921, demonstrated how light behaves as particles (photons) under certain circumstances. This discovery was critical in the development of quantum mechanics.
Applications in Modern Technology
- Solar Panels: The principles of the photoelectric effect are directly applied in photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. Einstein’s work laid the foundation for this renewable energy technology.
- Semiconductors: Quantum mechanics underpins the behavior of semiconductors, essential components of modern electronics, including computers, smartphones, and microchips.
- Quantum Computing: Einstein’s discussions on entanglement, famously calling it “spooky action at a distance,” have spurred advancements in quantum computing, which promises unprecedented processing power.
3. Lasers: A Direct Impact on Communication & Medicine

The concept of stimulated emission, a process Einstein introduced in 1917, is the principle behind the development of lasers. Although he couldn’t have envisioned its vast applications, lasers have revolutionized multiple industries.
Applications in Modern Technology
- Telecommunications: Fiber-optic communication relies on lasers for high-speed data transmission, enabling modern internet and communication networks.
- Medical Advances: Lasers are used in surgeries, vision correction (LASIK), and cancer treatment.
- Consumer Electronics: Laser technology is integral to devices like barcode scanners, CD/DVD players, and printers.
Einstein’s theoretical work indirectly sparked the creation of an essential technology that touches nearly every aspect of modern life.
4. Nuclear Energy: From Theory to Reality
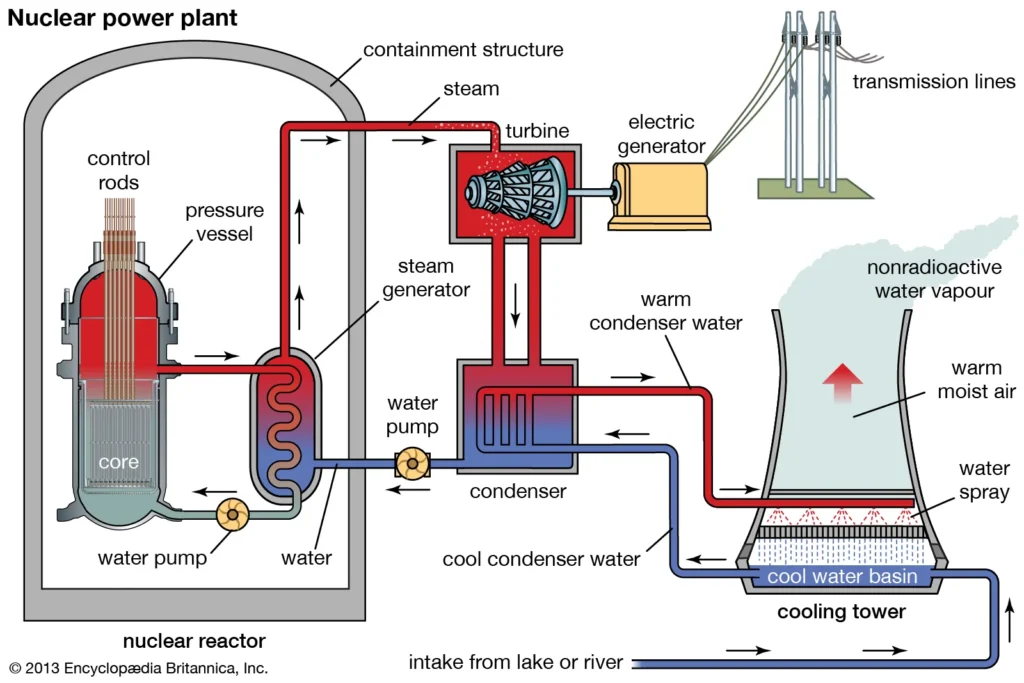
Source: Encyclopedia Britannica
Einstein’s equation E=mc2 demonstrated the vast energy contained in matter, a principle that became the basis for nuclear energy.
While Einstein himself did not directly develop nuclear technologies, his letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1939 (co-authored with physicist Leó Szilárd) warned of Nazi Germany’s potential development of atomic bombs, which led to the Manhattan Project.
Applications in Modern Technology
- Nuclear Power: Today, nuclear reactors generate electricity using the principles of nuclear fission, which relies on Einstein’s understanding of energy-mass equivalence.
- Nuclear Medicine: Techniques like PET scans and radiotherapy are based on nuclear physics.
- Weapons: Unfortunately, Einstein’s work also contributed to the development of nuclear weapons, though he later became an advocate for peace and disarmament.
5. Beyond Physics: Inspiring Innovation & Creativity

Einstein’s influence transcends physics. His emphasis on imagination, curiosity, and critical thinking has inspired generations of scientists, engineers, and innovators.
Key Philosophical Contributions
- Interdisciplinary Thinking: Einstein believed that creativity was essential for problem-solving. His approach to scientific inquiry has encouraged researchers across disciplines to think outside the box.
- Humanitarian Influence: As an outspoken advocate for peace, civil rights, and education, Einstein’s worldview continues to inspire leaders and thinkers worldwide.
6. Future Technologies Influenced by Einstein’s Theories

Even in the 21st century, Einstein’s work continues to drive technological progress:
- Gravitational Wave Detection: The detection of gravitational waves by LIGO in 2015 confirmed Einstein’s predictions from a century ago and opened a new field in astrophysics.
- Artificial Intelligence: Understanding the behavior of energy and matter at a quantum level contributes to advancements in AI and machine learning.
- Space-Time Manipulation: Theoretical research on concepts like warp drives and wormholes is based on Einstein’s relativity, offering possibilities for future space travel.
Challenges in Realizing Einstein’s Vision

Despite his significant contributions, some of Einstein’s ideas, such as a unified field theory, remain incomplete. Modern scientists continue to grapple with bridging the gap between relativity and quantum mechanics—a challenge Einstein himself worked on unsuccessfully.
How Can We Leverage Einstein’s Legacy?
To further innovation, we must:
- Invest in Fundamental Research: Einstein’s breakthroughs were born from pure curiosity. Governments and private sectors must fund basic science without immediate practical applications.
- Encourage Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Einstein’s genius lay in connecting seemingly unrelated concepts. Collaborative efforts across physics, technology, and philosophy can yield groundbreaking results.
- Promote STEM Education: Inspiring the next generation of scientists and innovators is crucial for advancing technologies rooted in Einstein’s principles.
Einstein’s Lasting Impact
Albert Einstein’s revolutionary ideas have shaped modern technology in ways he likely could never have imagined. From the devices we use daily to the renewable energy we harness; his theories remain the bedrock of countless innovations.
But perhaps Einstein’s greatest contribution is his reminder that the human capacity for curiosity, creativity, and wonder is boundless. His legacy urges us to explore not just the universe but also the infinite possibilities within ourselves.